The loss modulus see Figure 2. Shear modulus G Storage modulus M proportional to the energy stored elastically and reversibly Loss modulus M proportional to.

Ashby Plot Showing The Strength And Young S Modulus Of Polymers Yield Download Scientific Diagram
Similarly the loss modulus G or E of a material is the ratio of the viscous out of phase component.
.jpg)
G modulus polymer. G2 to 100 R g ie. EXPERIMENTAL SECTION PS M w 97 Kgmol M wM n 106 R g 10 nm and T g 100C was purchased from Polymer Source. It is a measure of the energy dissipation of a material.
The elastic modulus G obtained by stress-strain relationship was 70 Pa at ϕ 0129 which is slightly larger than the storage modulus G 2 Pa. G lim t G t displaystyle Glim _tto infty Gt. Storage modulus G elastic behavior loss modulus G viscous behavior limiting value of the linear viscoelastic LVE- range when reaching γγγL - at the given test conditions ie at the preset angular frequency - left side.
It can be seen from the formulathe modulus increases with temperature. Molecular weight M. For most engineering plastics ν is in the range 035 ν 045 see table of Poissons ratios.
The G refers to the elastic modulus and reflects elastic behavior of a material when deformed. D shows a behaviour similar to Λ EG. The shear modulusG for the polymers subjected to the small-strain conditions can be defined by GNkT where N is the number of network chains k is Boltzmanns constant and T is temperature in Kelvins.
Elastic or storage modulus G or E of a material defined as the ratio of the elastic in-phase stress to strain. Type of polymer Modulus E Pa Rubber 106 Semicrystalline polymer above Tg 10 8 Semicrystalline polymer below Tg 10 9 Glassy polymer 109 Semicrystalline polymer fiber 1010 Polymer single crystal fiber 1011 Table 1. However despite its technological importance the corresponding elastic modulus of the confined thin polymer films has yet to be fully characterized to the same extent as T g effects have been done.
PMMA M w 996 Kgmol Rg 9 nm T. The storage modulus relates to the materials ability to store energy elastically. Now the sponge itself has a certain rigidity that contributes to the complex modulus and because the sponge is an elastic solid we can think about this contribution as G.
160 rows The modulus of glass fibers is 72 GPa 105 x 10 6 psi The Youngs modulus of. The storage modulus either E or G is the measure of the samples elastic behavior. The ratio of the loss to the storage is the tan delta and is often called damping.
G G liquid - like structure in the LVE - range. Title Thermal conductivity of high-modulus polymer fibers abstract Polymers have many desirable properties for engineering systems-eg low mass density chemical stability and high strength-to-mass ratio-but applications of polymers in situations where heat transfer is critical are often limited by low thermal conductivity. The Youngs modulus did not change with thickness over the large range of film thicknesses we used in our experiment.
Both moduli G and G are of great importance to scientist and engineers since they can be correlated to basic polymer properties such as glass transition temperature T g entanglement weight M e degree of crystallinity crosslink density ν e and many other properties. From sub-molecular to the bulk. G G gel - like structure in the LVE - range right side.
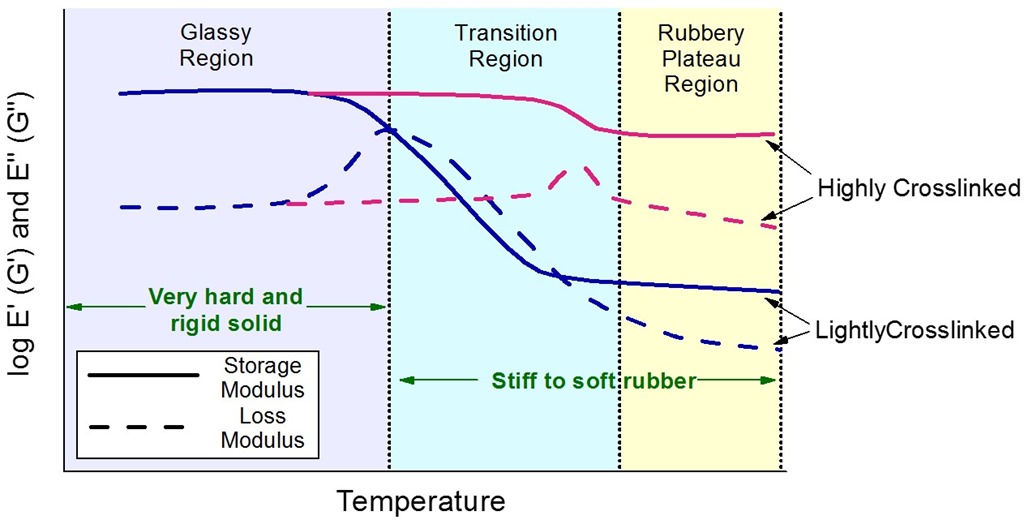
Shear-thinning is the most common form of non-Newtonian behaviour and is seen in suspensions emulsions polymer solutions and gels. The G refers to the viscous modulus which reflects the flow of a material while it is deformed. We already know that going from below to above the glass transition temp will have a dramatic effect on the modulus below T g the polymer is rigid glassy solid but above T g it begins to flow and the modulus decreases significantly.
Spectroscopy to study polymer morphology and structure and relate these to end-use performance. G d e f τ x y γ x y F A Δ x l F l A Δ x displaystyle G stackrel mathrm def frac tau _xygamma _xyfrac FADelta xlfrac FlADelta x where τ x y F A. Compatible and incompatible polymer mixtures or copolymers compared with the basic pure polymers.
At γ 02 G decreased drastically when γ increased whereas at larger γ than 10 G approached to a constant value. In materials science shear modulus or modulus of rigidity denoted by G or sometimes S or μ is a measure of the elastic shear stiffness of a material and is defined as the ratio of shear stress to the shear strain. Complex modulus is a useful property to quantify as it is a direct measure of the rigidity of a materials soft solid structure when exposed to stresses below the yield stress.
Wgoes to infinity System loses solubility Zero shear viscosity goes to infinity Equilibrium Modulus is zero and starts to rise to a finite number beyond the gel point Note. The presence of the stiffening groups such as amide sul-fone carbonyl p-phenylene etc in the polymer chain reduces the flexibility. Accurate solid state measurements of the materials glass transition temperature T g modulus G and damping tan δ are used to predict practical use temperatures impact pr operties energy dissipation stiffness and many other performance.
For a hypothetical material with no lateral contraction ν 0 the elastic tensile modulus is about two times the shear modulus and three times the bulk modulus. The fourier transform of the shear relaxation modulus G t displaystyle Gt is G ω G ω i G ω displaystyle hat Gomega hat Gomega ihat Gomega see below. In the figure below we consider the effect of temperature on the modulus for polymers at a given time and strain.
For visco-elastic solids converges to the equilibrium shear modulus. Direct experimental measures of the ultrathin material modulus have proven to be difficult since the presence of stiff substrate tends to interfere with the measurements 8. G 80C has stronger intermolecular forces than polypropylene T g 18C because of the dipoledipole forces from the CClbond.
E 2 G 3 B. Q How does the storage modulus in a DMA run compare to Youngs modulus. At the Gel Point.
7 is even more frequency-depend-. Modulus of various polymers Although the above relationship for stress and strain cannot be applied to complex. Complex shear modulus G the Young modulus E and the complex viscosity η can be visualized as the damping factor D is then given by the tan of the loss angle δ Dtan.
E 83 G and E B. Correlation between moduli and phase angle damping.

Different Stages Of The Relaxation Modulus Of A Polymer Melt See Text Download Scientific Diagram

Polymers As Solids Matse 202 Introduction To Polymer Materials
Practical Tips For Curing Thermosets Part Eight The Glass Transition Temperature Measured Using Dma Polymer Innovation Blog

